Break Even Point Calculator: Mastering Business Profitability
In the world of business, profit and cash flow are often emphasized as the ultimate measures of success. However, it’s important to remember that your business’s financial health may remain uncertain without a solid understanding of your break-even point.
Understanding and accurately calculating your company’s break-even point is vital for assessing profitability and making informed decisions. Our Breakeven Calculator helps you discover your true breakeven point. Below you will find a step by step guide on how to use it, and why it is more accurate than other breakeven calculators floating around on the internet.
What is the Break-Even Point?
The break-even point is the pivotal moment where your sales revenue matches your total costs, both fixed costs and variable costs. Calculating and analyzing this critical number gives you valuable insights into your business’s profitability and viability.
The Raw Break-Even Point
Traditionally, the break-even point is seen as the moment when your business neither makes a profit nor incurs a loss. It’s when your sales cover all your fixed and variable costs. However, this perspective fails to account for drawings or dividends and the associated tax implications. To gain a more accurate picture, we need to consider these factors and calculate the break-even point accordingly.
Calculating the Actual Break Even Point
The internet is flush with breakeven calculators measuring raw breakeven; however, few take into account the above. So Quantum Advisory has developed our own calculator that accounts for drawings or dividends and the associated tax implications. You can download it here.
The following is a Step-by-Step Guide to calculating your true break-even point using our calculator.
1. After-Tax requirements
Start with the often overlooked after-tax requirements, which include drawings or dividends and debt obligations.
Determine Drawings or Dividends:
No doubt you have owner’s or director’s wages in your overhead costs, but perhaps you need to draw down on funds in addition to these wages, or maybe you need to allow for a certain amount of dividends to be paid out to shareholders, either way, you need to account for these amounts as they come out after the net profit line. Enter this figure into the calculator. For this example, let’s assume $250,000 is required for drawings.
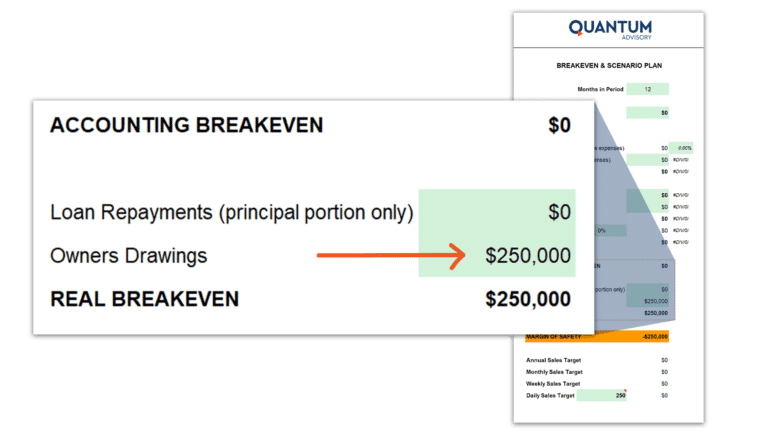
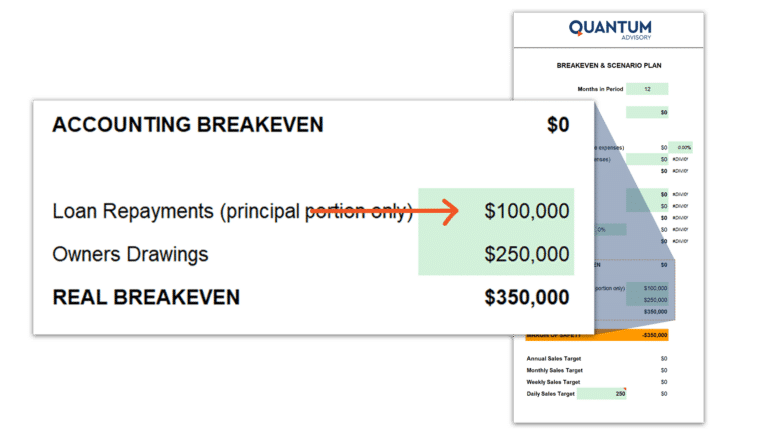
Consider Debt Obligations:
Interest on borrowings is included in your overhead costs; however, the principal or loan amortization (the amount of principal and interest paid each month over the course of your loan term) isn’t. Enter this figure into the calculator.
If, for instance, you want to allow for $100,000 of debt repayment. This will combine with drawings, resulting in an after-tax requirement of $350,000. That is, you’ll need $350,000 in profits after allowing for tax to cover your drawings and debt repayments
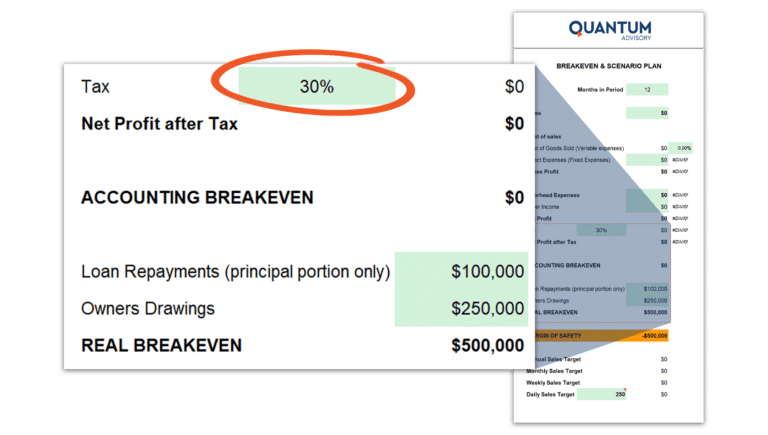
Incorporate Tax Considerations:
The calculator will then allow for tax on these profits. Simply enter your tax rate.
If we allow for a tax rate of 30%, the tax amount on that $350,000 would be $150,000. Thus, the total requirement before tax stands at $500,000.
So we can see here how are raw break-even analysis doesn’t give you your true breakeven point, as the raw breakeven at this point would be nil, whereas a realistic breakeven requires $500,000 in net profit.
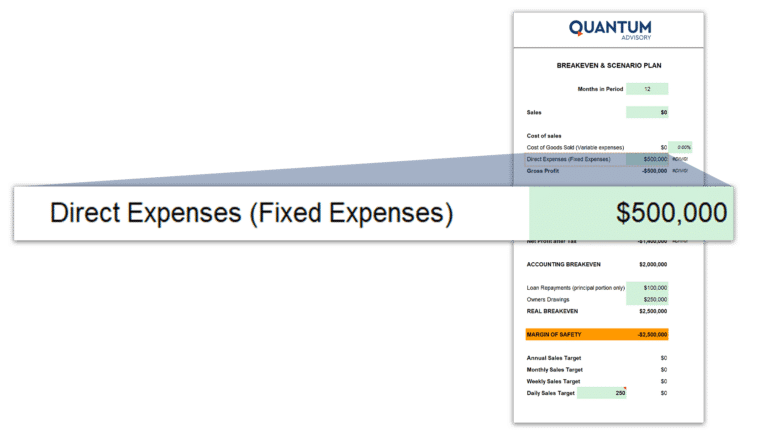
2. Identify Costs
Once you’ve sorted out your after-tax requirements and allowed for tax on that, the next step is to enter your costs which are broken down into three areas:
Fixed Costs:
Fixed costs refer to expenses that remain constant regardless of the level of production or sales. These costs do not vary with the volume of output and include items like rent, salaries, insurance premiums, and equipment maintenance.
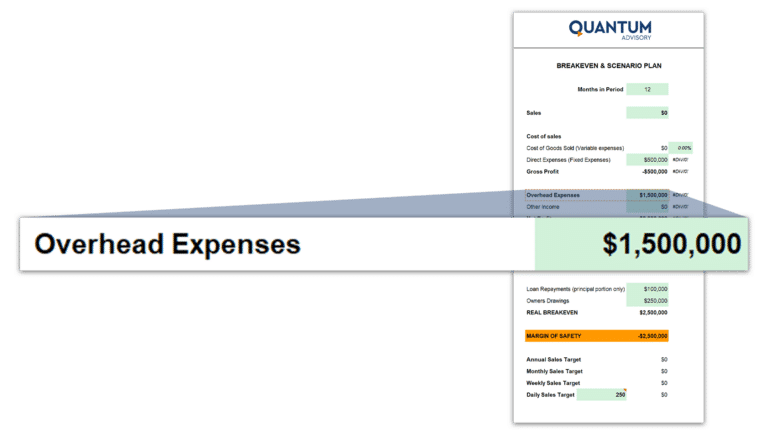
Overhead Costs:
Overheads encompass all the ongoing expenses necessary to run a business that are not directly tied to production. This includes costs such as utilities, office supplies, marketing expenses, and administrative salaries.
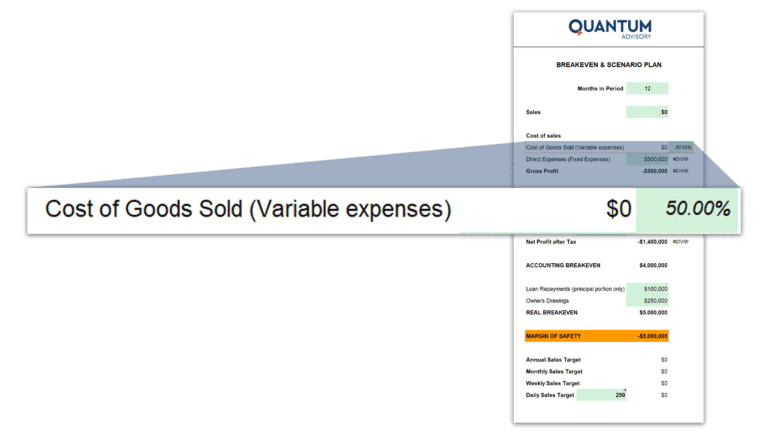
Cost of Goods Sold (COGS)/Variable Costs:
COGS or variable costs, such as raw materials, packaging, and shipping costs, that vary with how many units are produced or sold.
As they are variable, this needs to be entered into the calculator as a percentage. To get your COGS percentage, follow this formula:
COGS Percentage = Total Variable Costs / Sales
So in this example, your total variable costs are $3,000,000 and let’s say your sales are $6,000,000, the calculation would be:
COGS Percentage = $3,000,000 / $6,000,000 = 50%
As an aside, if you wanted to calculate your contribution margin, generally, you would deduct the variable cost from the unit price or selling price. However, given we’ve calculated the COGS percentage, we can assume the remaining per cent represents the contribution margin.
3. Let the Breakeven Calculator Do Its Thing
Once you’ve entered all your details, the break-even point formula in the calculator will instantly provide you with your TRUE breakeven point. It’s as simple as that.
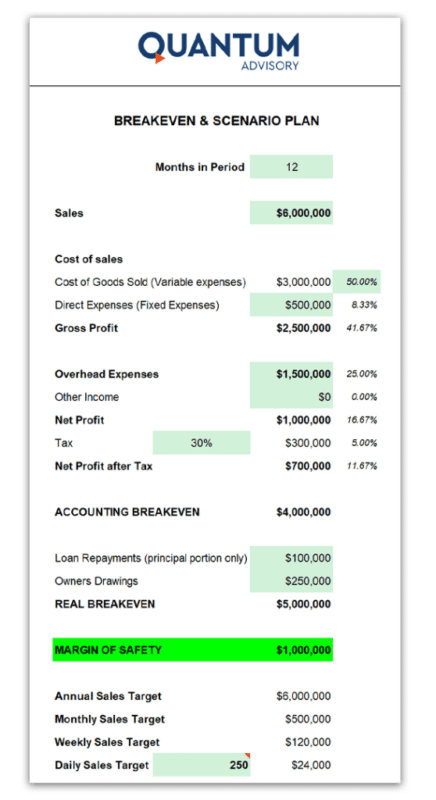
Analysing Breakeven Calculator Results
Once you have calculated the break-even point, you can leverage the information to make informed business decisions:
Assess Profitability:
Compare your company’s breakeven point with the actual number of units sold. The breakeven calculator allows you to enter your sales and automatically incorporates it into the data. You generate a net profit if your sales volume surpasses the break-even point. Conversely, you incur a loss if your sales fall below the break-even point.
Evaluate Pricing Strategies:
By understanding your break-even point, you can determine the minimum price per unit required to cover costs and achieve profitability. This knowledge empowers you to set competitive prices that not only cover expenses but also contribute to your gross profit.
Identify Cost Optimisation Opportunities:
The breakeven calculator allows you to identify areas where you can reduce costs. Analyse your fixed and variable costs to uncover potential savings without compromising product quality or customer satisfaction.
Conduct “What-If” Scenarios:
Utilize the breakeven calculator to explore different scenarios and determine how changes in costs, pricing, or sales volume impact your break-even level. This analysis provides valuable insights into various business strategies’ potential risks and rewards.
Mastering your company’s break-even point is essential for evaluating profitability, setting prices, and making informed decisions. By incorporating fixed and variable costs, conducting break-even analysis, and utilizing a break-even point calculator, you better understand your business’s financial health. Regularly revisiting and adjusting your break-even point analysis enables you to adapt to market fluctuations, optimize costs, and ensure the long-term success of your business.

